Uno dei maggiori limiti delle fonti rinnovabili, in particolare quelle derivanti dal vento e dal sole, è la loro intermittenza e la non programmabilità nel tempo. Lo sviluppo su larga scala dell’energia eolica e fotovoltaica richiede la crescente disponibilità di sistemi e tecnologie per l’immagazzinamento dell’energia, in grado di assorbire i picchi di potenza dalle fonti rinnovabili e renderli disponibili quando vi è domanda di energia dalla rete.
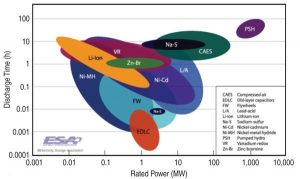
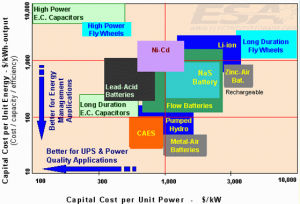
Vi sono numerose tecnologie utilizzabili per l’accumulo energetico, con caratteristiche molto diverse in termini di fascia di potenza e di tempi necessari al rilascio dell’energia, oltre che di costi e di modalità di utilizzo. Come è evidenziato dai dati presentati dall’ESA, le soluzioni demandate all’accumulo chimico con i diversi tipi di batterie coprono la fascia delle potenze medio-basse, mentre sulla fascia delle potenze medio-alte lo spazio è occupato soprattutto dall’accumulo idro-elettrico (PSH) e dal CAES. Quest’ultima tecnologia presenta costi unitari più contenuti rispetto ai concorrenti, in termini di costi per unità di potenza e per unità di energia stoccata.
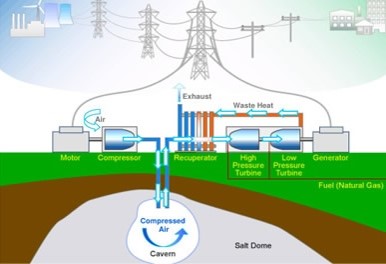
Sulla base di studi e ricerche sull’accumulo pneumatico (Compressed Air Energy Storage, CAES) svolte all’Università di Salerno a partire dal 2005, ePowerIng collabora con InElectric ed altri partner istituzionali ed industriali all’obiettivo di progettare e realizzare impianti di accumulo con caratteristiche innovative, per far fronte alla prevista crescita della generazione energetica da fonti rinnovabili prevista dal PNRR. Uno studio finalizzato alla realizzazione di impianti pilota nella regione Basilicata è stato presentato a Dubai il 24 marzo 2002. Le slide sono disponibili qui: CAES_Dubai.

One of the major limitations of renewable sources, especially those deriving from the wind and the sun, is their intermittence and non-programmability over time. The large-scale development of wind and photovoltaic energy requires the growing availability of energy storage systems and technologies capable of absorbing power peaks from renewable sources and making them available when there is a demand for energy from the grid.

There are numerous technologies that can be used for energy storage, with quite different features in terms of power range and release time, as well as costs and use. As evidenced by the data presented by ESA, the solutions assigned to chemical storage with the different types of batteries cover the medium-low power range, while the medium-high power range space is mainly occupied by hydro- electricity (PSH) and by CAES. This latest technology has more favorable unit costs than its competitors, in terms of costs per unit of power and per unit of stored energy.

Based on studies and research on pneumatic storage (Compressed Air Energy Storage, CAES) carried out at the University of Salerno since 2005, ePowerIng collaborates with InElectric and other institutional and industrial partners with the aim of designing and building storage systems with innovative features, to cope with the expected growth of energy generation from renewable sources envisaged by the PNRR. A project (WE-Exergy) aimed at the construction of pilot plants in the Basilicata region was presented in Dubai on 24 March 2002. The slides are available here: CAES_Dubai.
References
Arsie, I Marano, V Nappi, G and Rizzo, G (2005 ) “A model of a hybrid power plant with wind turbines and compressed air energy storage” in ASME Power Conference ( IL), Vol 41820 987 1000 ISBN/ISSN 0 7918 4182
Arsie, I Marano, V Rizzo, G Savino, G and Moran M (2006 ) “Energy and economic evaluation of a hybrid CAES/Wind power plant with neural network based wind speed forecasting, 19 th International Conference on Efficiency, Cost, Optimization, Simulation and Environmental Impact of Energy Systems AGHIA PELAGIA, CRETE ( JULY 12 14 2006)
Arsie, I Marano, V Moran, M Rizzo, G and Savino, G (2007 ), “Optimal management of a wind/CAES power plant by means of neural network wind speed forecast” in European Wind Energy Conference and Exhibition, The European Wind Energy Association (EWEA)
Arsie I Marano V Rizzo G Moran M 2009 Integration of Wind Turbines with Compressed Air Energy Storage In POWER CONTROL AND OPTIMIZATION Proceedings of the Second Global Conference on Power Control and Optimization, Bali
Arsie I Marano V Moran M Rizzo G 2009 Potentialities of CAES (Compressed Air Energy Storage) and V 2 G (Vehicle to Grid) in the Electricity Market Optimization and in the Integration of Renewable Resources In 2nd Power Make Up Conference POMAC 2009 15 17 November 2009 Marriot Courtyard Hotel, Kuwait
V Marano, G Rizzo, F A Tiano 2011 Application of Dynamic Programming to the Optimal Management of a Hybrid Power Plant with Wind Turbines, Photovoltaic Panels and Compressed Air Energy Storage In ICAE 2011 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON APPLIED ENERGY, PERUGIA CENTRO CONGRESSI, PERUGIA, ITALY MAY 16 2011 MAY 18 2011
Marano, V Rizzo, G and Tiano, F A 2012 Application of dynamic programming to the optimal management of a hybrid power plant with wind turbines, photovoltaic panels and compressed air energy storage Appl Energy 97 849 859 doi 10 1016 /j apenergy 2011 12 086
Tiano, F A Rizzo, G and Marra, D 2018 Design and optimization of a charging station for electric vehicles based on compressed air energy storage IFAC PapersOnLine 51 230 235 doi
10 1016 /j ifacol 2018 07 038
Tiano F A Rizzo G 2021 Use of an Under Water Compressed Air Energy Storage to Fully Power the Sicily Region with Renewable Energy A Case Study, Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering,
Vol 7 https :://www frontiersin org/article/ 10 3389 /fmech 2021 641995 DOI= 10 3389 /fmech 2021 641995 ISSN= 2297 3079